every manip u do to a java String object will return a COPY of that manipulated String.
this is so anything pointing (pointers/ref) to a string in memory will still have the same String there.
your NEW variable will have a new string but it will be at another address in the heap.
String pool (String intern pool) is a special storage area in Java heap. When a string is created and if the string already exists in the pool, the reference of the existing string will be returned, instead of creating a new object and returning its reference.
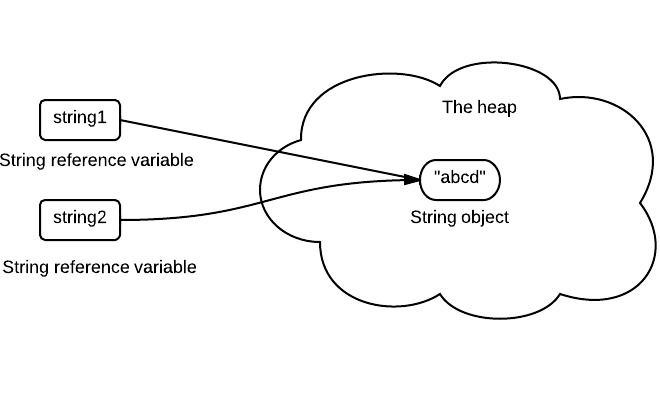
The following code will create only one string object in the heap.
1.String string1 = "abcd";2.String string2 = "abcd";Here is how it looks:
If string is not immutable, changing the string with one reference will lead to the wrong value for the other references.
2. Allow String to Cache its Hashcode
The hashcode of string is frequently used in Java. For example, in a HashMap. Being immutable guarantees that hashcode will always the same, so that it can be cashed without worrying the changes.That means, there is no need to calculate hashcode every time it is used. This is more efficient.
3. Security
String is widely used as parameter for many java classes, e.g. network connection, opening files, etc. Were String not immutable, a connection or file would be changed and lead to serious security threat. The method thought it was connecting to one machine, but was not. Mutable strings could cause security problem in Reflection too, as the parameters are strings.
4. collection safety. maps don't support mutations of keys, and strings are the most popular object to use as a key
5. defensiveness, you don't have to worry about a method you are calling changing the string out from under you
6. performance, there is an additional level of indirection needed to support sharing strings across some mutations (like growing the string)
7. thread safety/performance. the easiest way to guarantee safety and to cut down on use of synchronized blocks is to make your data immutable.
No comments:
Post a Comment